Introduction
The term Industry 4.0 is commonly mentioned in discussions around Digital Transformation, but what does it actually mean? Industry 4.0, also known as the Fourth Industrial Revolution, represents a significant shift towards smart, interconnected systems that integrate the physical and digital worlds. Driven by advanced technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), Big Data, artificial intelligence, and advanced automation, Industry 4.0 is reshaping industries on a global scale.
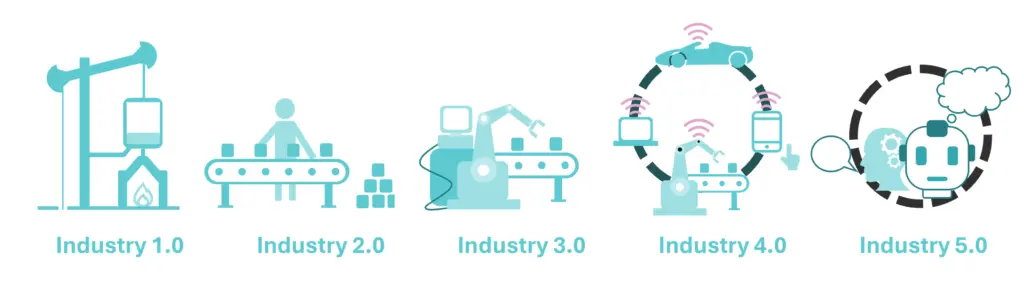
Looking ahead, Industry 5.0 promises even greater advancements, focusing on more refined human-machine collaboration and personalised automation. To truly understand this progression and the broader Digital Transformation journey, it’s essential to explore the timeline of Industrial Revolutions that have led us to this point.
The Industrial Revolution Timeline

Industry 1.0 (1784)
The First Industrial Revolution marked a monumental shift from manual labour and animal power to mechanised production. Key innovations included:
- Mechanisation using steam power, transforming industries like textiles.
- The development of steam-powered transportation, such as trains, revolutionising how goods and people moved.
Industry 1.0 laid the foundation for industrialisation by introducing machinery, leading to greater efficiency and productivity.
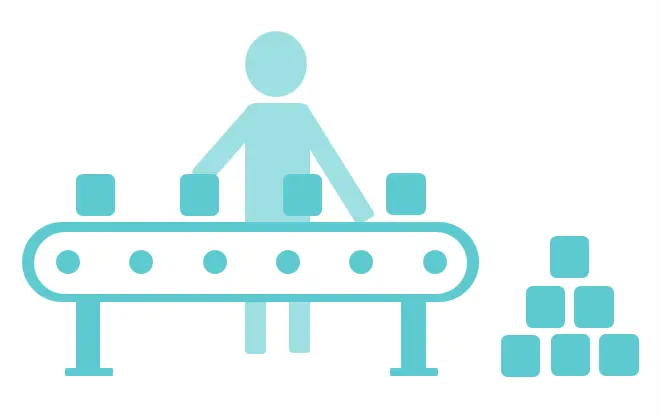
Industry 2.0 (1870)
The Second Industrial Revolution brought about mass production and more efficient manufacturing processes, thanks to the following innovations:
- The introduction of electrical energy, enabling assembly lines and large-scale production.
- The development of the internal combustion engine, giving rise to the automotive industry.
- The emergence of communication technologies, including the invention of radio and the advent of mass media through television.
This era dramatically increased production capabilities and improved connectivity, further transforming economies and societies.
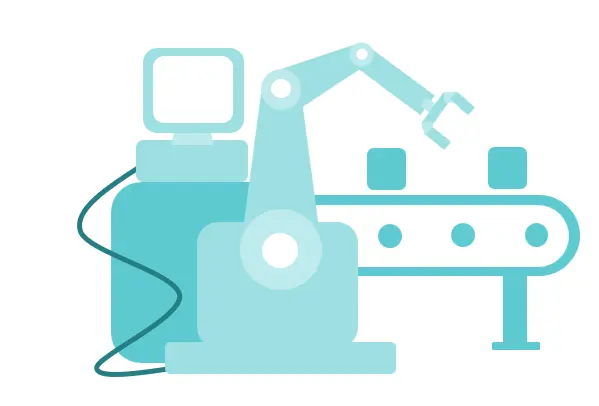
Industry 3.0 (1969)
The Third Industrial Revolution, also known as the Digital Revolution, saw the advent of electronics, computing, and early automation. Notable advancements included:
- The rise of electronics and the widespread use of semiconductors.
- Early computing systems that laid the groundwork for data management and automated processes.
- The emergence of information technology, fundamentally changing how industries operate and paving the way for global communication networks.
This revolution marked the beginning of digitisation, reshaping industries with new technologies and setting the stage for more sophisticated automation.
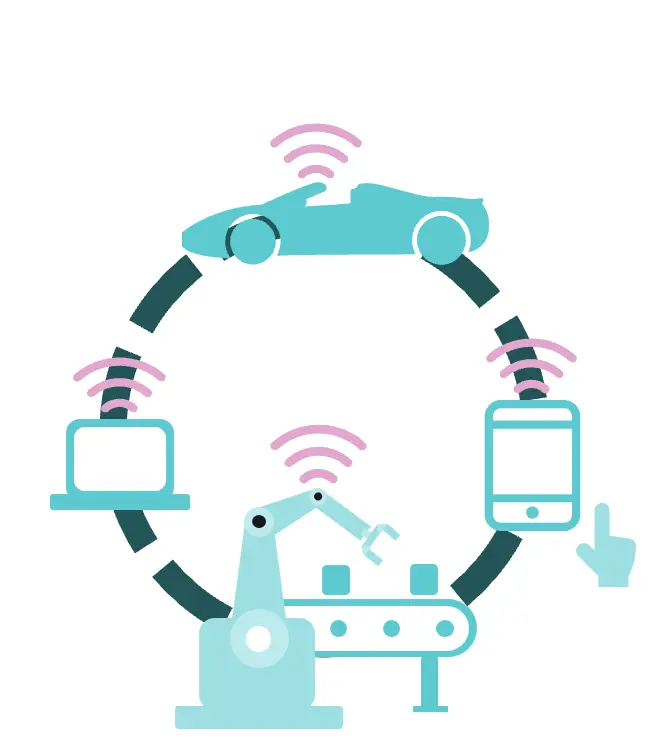
Industry 4.0 (Today)
The Fourth Industrial Revolution is characterised by the integration of digital, physical, and biological systems. Key technologies driving Industry 4.0 include:
- Cyber-physical systems: Combining physical processes with digital feedback loops.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Connecting devices and systems for real-time monitoring and optimisation.
- Big Data and Cloud Computing: Providing data-driven insights and scalable computing power.
- Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence: Automating complex tasks and enabling predictive analytics.
- Advanced Robotics: Developing robots capable of performing intricate tasks with precision.
- 3D/4D Printing: Revolutionising manufacturing processes with rapid prototyping and complex design capabilities.
- Blockchain: Enhancing data security and transaction transparency through decentralised systems.
Industry 4.0 has transformed manufacturing and operations, making processes smarter, more efficient, and more adaptable to changing demands.
Industry 5.0 (Tomorrow)
Looking ahead, Industry 5.0 focuses on human-centric and sustainable advancements. Future trends include:
- Human-Machine Collaboration: Refining the way humans and robots work together, using AI to provide meaningful and personalised interactions.
- Customised Automation: Leveraging technology to cater to individual preferences and enhance user experience.
- Sustainability and Ethics: Emphasising eco-friendly practices and responsible technology use to ensure long-term benefits for society.
Industry 5.0 represents a more holistic approach, where technology enhances human capabilities while addressing social and environmental concerns.
Conclusion
From the mechanisation of the 18th century to today’s interconnected systems, each Industrial Revolution has brought profound changes to how we live and work. Industry 4.0 continues to transform industries, making them more intelligent and efficient, while Industry 5.0 promises to take this further, focusing on human-centered design and sustainability. Understanding this timeline not only highlights the progress we’ve made but also prepares us for the ongoing Digital Transformation journey, as we embrace a future where technology and human ingenuity continue to shape our world.
